The desert rose is beautiful and very easy to care for. It’s a great plant to give as a gift to your loved ones, as it doesn’t need a lot of attention.
As long as you follow the tips and guides in this post, it should last you centuries!
Table of Contents
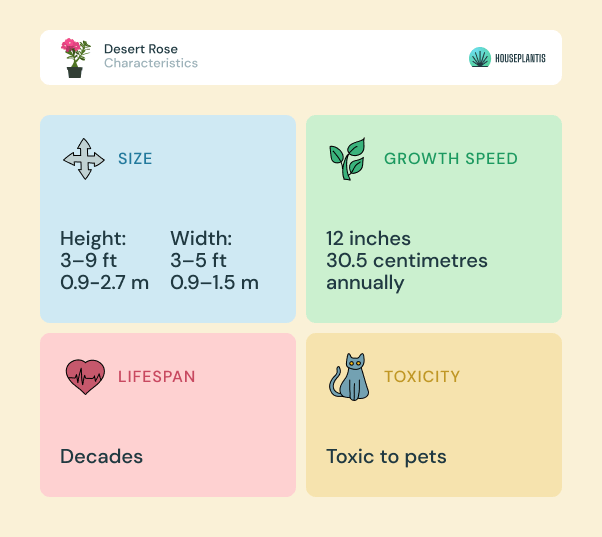
Main Characteristics
Despite what you may think when you first hear desert rose, it’s actually not a rose at all. It’s part of the Apocynaceae family and has beautiful trumpet-shaped flowers, shiny green leaves, and a thick trunk that resembles a bonsai plant.
Its flowers are grown in a combination of different colors such as pink, purple, red, and white.
Its scientific name is Adenium obesum and is native to Africa, Madagascar, and the Middle East. The desert rose is very simple to grow and doesn’t need much maintenance because of its ability to withstand heat and drought. In times of extreme drought, it can store water in its trunk to save for later.
Depending on the environment where it’s cultivated, it may be grown outdoors or indoors. Adenium is an evergreen plant, meaning its leaves remain intact throughout the next growing season.
Size
The desert rose grows between 3 to 9 feet (91.44 – 274.32 cm) tall and 3 to 5 feet (91.44 – 152.4 cm) wide, depending on where it’s grown and the climate. Because it favors the outdoors, it can prosper to about 9 feet (~2.5 m) tall and 4 feet (~1 m) wide in hot climates.
Growth Speed
It has a relatively slow-growing rate and grows roughly 12 inches (30.5 cm) per year but can be much less. Most commonly, after three years, the average height is just 14 inches (35.5 cm).
Lifespan
A desert rose that is well-cared for can live for decades. However, it will die if kept in frigid temperatures. Overwatering can also harm them since they are prone to root rot.
Is It Poisonous?
Just like the calla lily, the Adenium’s sap can be toxic to humans and animals if ingested. Wear gloves when handling the plant as it can irritate the skin.
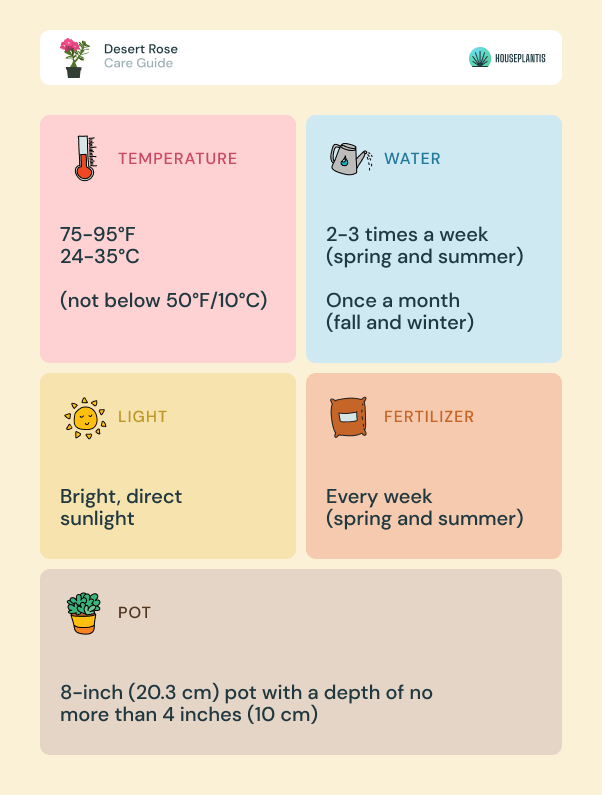
Care
Here is some vital information on how to care for the desert rose!
How Often to Water
Depending on the temperature and season, the desert rose has different water needs. Throughout late spring and summer (growing season), the soil should be kept moist. It shouldn’t ever be soaked, however, as this can lead to overwatering.
It might need to be watered around 2 to 3 times a week. The soil should be checked every few days and completely dry before watering again, much like one would do when watering the panda plant.
An Adenium’s trunk is an excellent indication of whether or not it’s getting enough water. A thick, swollen trunk is a good sign that it’s getting the right amount of hydration.
You may considerably minimize how much water it’s getting during winter and fall by just watering about once a month.
Drainage
Ensuring the proper drainage for your desert rose is a crucial step to prevent its root from rotting. A good tip is to place your desert rose in a pot with drainage holes (or drill some in yourself). Using a terra cotta or clay pot can also assist with extra moisture.
To improve drainage within the soil, you can combine two parts of commercial potting mix and 1 part perlite.
Pruning
While trimming or handling an Adenium, keep in mind that the sap is toxic. Wear gloves so that it doesn’t come in contact with your skin. If it does, use soap to wash it off right away, as the sap can irritate your skin.
If you’re pruning multiple different plants, disinfect your pruners between each one with rubbing alcohol or a bleach solution. When new growth develops, remove any damaged branches from the tip.
For the stems to develop proportionately, trim the long and slim stems. Cut slightly above a leaf node or where the stem connects with another to remove branches that touch or overlap with other growths.
You’ll also want to prune where stems and branches cluster together to provide more space for the plant.
Repotting
The desert rose can only be planted in soil and not water. As with trimming, you’ll also want to wear gloves while repotting to avoid getting any of the toxic sap on your skin. The optimum time to repot a desert rose is in late winter or early spring, ideally as soon as new growth appears.
Depending on how big you want your Adenium to grow, you’ll want to replant it yearly or every other year, as they grow very slow. You will also need to repot if its thick stem has grown and overcrowded the container, as they are known to crack and burst through pots.
The size of the container or pot it’s in ultimately determines how big the plant will grow. It would be best if you replanted it in a 1 to 2 inches (2.5 – 5 cm) container wider than its previous container, along with adequate drainage holes.
To guarantee a well-draining soil, use a cactus or succulent potting mix. You can also use average potting soil combined with equal amounts of perlite or sand instead.
The steps for repotting your desert rose are as follows:
- Gently remove the plant from the pot. You may have to wiggle it out a little.
- Remove any of the older soil from around and in-between its roots along. Remove all of the rotted or dead roots you find and treat the cuts with a fungicide.
- Then transfer it into its new pot, spreading the roots widely.
- Fill the pot with the soil, but make sure to leave its caudex (the thick part of the stem) exposed (if it’s at least three years old) about 1 or 2 inches (2.5 – 5 cm) above the soil.
After repotting, wait a week to water it to prevent shocking it. When you water it again, be sure that it drains completely and never allow it to sit in water. You should also gradually introduce it to sunlight again over several weeks, as keeping it exposed to light can burn the caudex.
Environment
For the desert rose to prosper, it needs the best environment.
Sunlight
The desert rose flourishes in full sun, just like the croton plant, so make sure to pick a location in your home where it will get enough bright light throughout the day, which could be on a windowsill or in a sunroom.
If you can grow your plant outside, choose somewhere that gets a good amount of sunlight, not shaded by trees, but provides some shade from the sun throughout the late afternoon. Too much harsh sunlight can burn its leaves.
The University of Florida IFAS Extension suggests giving your Adenium plenty of bright and direct light during the summer.
An indoor plant should receive light at least six hours per day, while an outdoor plant should get full sunlight throughout the whole day for optimal growth. Plants that are maintained in the shadow will not bloom.
Soil
The desert rose, similar to that of the African violet, favors rich and well-draining soils. For optimum growth, use a potting mix enriched in organic matter, like peat.
Using heavy combinations can promote root rot as they usually retain moisture. The Adenium’s soil should be neutral to acidic with a pH of approximately 6.0 for proper development.
Fertilizer
For an extra boost of nutrients, you can give your plant liquid fertilizer. Outdoor plants need a balanced, water-soluble one. They should only be given the fertilizer every month during its growing season (spring and summer), not winter, which is its dormant season.
Indoor desert roses should be given fertilizer every week in their growing season. They need a water-soluble fertilizer diluted by half.
While it doesn’t need much feeding, it does require at least some to ensure that it gets the nutrients it needs to blossom.
Pot
A shallow, wide container is preferable over a deep pot for the desert rose. They also thrive in clay or ceramic as they absorb moisture better than plastic. If you use a catch dish, always ensure it’s not sitting in water to prevent them from rotting.
It’s best to use an 8-inch (20.3 cm) pot with a depth of no more than 4 inches (10 cm).
Temperature
The desert rose prefers continuously warm temperatures. It grows best in 75 to 95 degrees Fahrenheit (24 – 35 degrees Celsius). It shouldn’t be exposed to temperatures less than 50 degrees Fahrenheit (10 degrees Celsius); otherwise, it will die.
If you live in colder regions, you can move it inside during the winter and put it back outside when it gets warmer in spring. If you’re in an area where it is warm out during the day and cooler at night, you should bring it in during the night.
Humidity
The desert rose thrives in dry, hot climates, so you don’t have to worry too much about the humidity if it’s outside. They can also take low humidity and will be fine indoors.
Indoors vs. Outdoors
Desert roses may be grown outside in USDA plant hardiness zones 11 to 12. Otherwise, they can be kept inside.
As mentioned before, you can keep it outside during warmer temperatures but bring it in during colder times of the year.
Blooming
The Adenium generally blooms during the spring and summer over many weeks. In some cases, it may take longer for a plant to flower.
However, if the Adenium is healthy and in the right growing conditions, it will bloom eventually. It’s also possible for some plants to bloom year-round if adequately cared for.
If your Adenium isn’t blooming, it could be for a few different reasons:
- Repotting. If you repotted it recently, it might need time to adjust to its new surroundings. Since you will be repotting it into a wider pot, it will focus its energy on growing roots instead of producing blooms.
- Water & Drainage. The desert rose can survive in droughts and live weeks without any water. However, they do need water to be able to produce blooms. Overwatering and improperly drained soil, on the other hand, can cause the Adenium to stop producing flowers and may even kill it by giving it root rot. Make sure you’re following the watering guide above for the best times to water your adenium.
- Sunlight. The Adenium needs sunlight to thrive. If it isn’t getting enough sunlight, this could be the cause for it not blooming. You may want to move your Adenium to a spot where it receives at least five to six hours or more of sun per day.
- Fertilizer. As previously mentioned, desert roses don’t need a lot of fertilizer. That being said, feeding it will give it the nutrients it needs to produce blossoms. Follow the directions given under the fertilizer section in this post for how to feed your plant correctly.
Propagation
Growing an Adenium from seed or cuttings is really simple! As long as you follow the instructions on how to do so, your desert rose should be growing in no time!
From Seeds
When it comes to desert rose seed beginning, the most important thing to remember is to start with fresh seeds. Fresh Adenium seeds will germinate quicker and have a greater germination rate.
The steps to seed propagation are as follows:
- Prepare a container with a well-draining growing medium. The growing medium could be perlite or a sand and soil blend. Then, place the seed inside and cover it with the growing medium.
- Water once a day from below and once every three days from above until seedlings emerge.
- Maintain the temperature of the growing medium between 80 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit (27 – 29 Celsius) by placing the tray or container on a heating pad.
- If the seeds are fresh, your plant should germinate within one week. If the seeds are not fresh, they may take longer or not grow at all.
- After the seedlings have appeared, water just from below. The seedlings will be large enough to transfer into a permanent container in around a month.
From Cuttings
While it is possible to cultivate an Adenium from seed, most gardeners find that cuttings are more successful. They start to grow faster and easier from cuttings and maintain the genuine character of hybrid plants, which would otherwise change if produced from seed.
The instructions are relatively straightforward:
- As with trimming, you should also wear gloves while propagating and use sterile pruners. Prepare a container with perlite or a sand and soil blend (you want it to be well-draining).
- Begin by cutting 5 to 6 inches (13 – 15 cm) from the tip of the branch.
- Let the cutting dry for one to two days. Once it’s dried, wet the tip of the cut and dip it in rooting hormone.
- Plant the cut about 2 inches (5 cm) into the soil mixture.
- Water it daily, checking to make sure the water drains well out of the soil.
The cutting should begin to take root in around two to six weeks. You can check after six weeks by tugging gently at the stem. It should feel rooted in the soil.
Reviving
If you’re growing an Adenium for the first time, you might be worried about its leaves changing color and not looking healthy anymore. We’ll go over what to do in this case!
Leaves Turning Yellow
Yellowing leaves or losing leaves suddenly can be a consequence of root rot. Root rot is caused by a fungus, usually after overwatering the plant and not having proper drainage.
You might be able to preserve it if you catch it early enough. You need to remove damaged leaves and stems, and the root ball should be unpotted. If you find any blackened or mushy roots, use a sharp knife to chop them out.
Make sure to sterilize the knife in between cuts. In a well-draining potting mix, replant the remaining root.
If that doesn’t seem to be the issue, yellow leaves can also indicate the Adenium is not receiving enough sunlight. Move the plant to an area where it will get at least five to six hours of direct sunlight.
Leaves Turning Brown
If the leaves begin to turn brown, this can indicate that the plant isn’t getting enough moisture or the proper nutrients. To figure out which one it is, try solving one at a time. First, check to see if it’s not getting enough water by increasing how much you’re watering it to twice a week.
If this doesn’t seem to be the issue, you may want to feed your plant some fertilizer. Look to the fertilizing sections of this post on how to feed your Adenium correctly.
Spotting on Leaves
Almost all plants are susceptible to powdery mildew, and desert rose is no different. Powdery mildew can form from high humidity at night and low humidity during the day. It also favors temperatures between 70 to 80 degrees Fahrenheit (22 – 27 Celsius). These conditions are most common during the spring and fall.
When its stems and branches begin to clump together, prune them out; having enough space between plants minimizes the possibility of powdery mildew forming.
Speckling of Lower Leaves
The most common pest to attack an Adenium is spider mites. They get their food by sucking sap from the underside of leaves. Leaf speckling will lead to total discoloration and eventually leaf death.
To check if spider mites are the culprit of your leaf speckling, shake a diseased plant over a piece of white paper. The spider mites will appear as tiny dots. You’ll also be able to notice webs and eggs on the underside of the leaves.
Conclusion
Desert roses are a relatively low-maintenance plant. They are easy to care for because of their resilience to drought and most other pests and illnesses.
If you follow these tips and instructions on how to give your plant the best conditions, the Adenium can live for centuries.